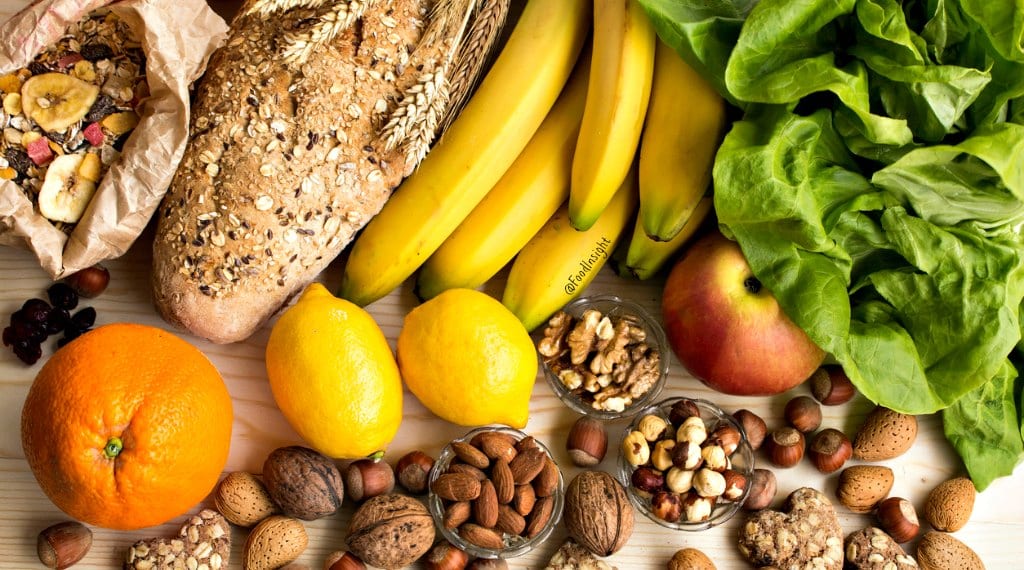
What are some of the good Foods with Minerals?
Minerals are components that are found in the earth and food and are necessary to live. For instance, minerals are needed for heart and brain function, as well as the production of hormones and enzymes.
Minerals are divided into two types established on how much the human body needs. Macrominerals are required in larger amounts and contain calcium, potassium, sodium, chloride, phosphorus, and magnesium
Although equally important, hint minerals, including iron, copper, fluoride, selenium, zinc, chromium, molybdenum, iodine, and manganese, are required in smaller amounts
Minerals can be found in a variety of foods, but some foods are predominantly generous in these important nutrients.
In this article, we will discuss some food with minerals.
Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are sealed with an array of minerals but are particularly prosperous in magnesium, zinc, manganese, copper, selenium, and phosphorus.
Specific nuts and seeds stand out for their mineral range. For instance, just one Brazil nut delivers 174% of your daily selenium requirements, while a 1/4-cup (28-gram) serving of pumpkin grains delivers approx 40% of your daily magnesium requirements.
Whole nuts and seeds create a convenient, nutrient-dense snack, while nut and seed butter can be blended into smoothies and oatmeal or paired with refreshed fruit or vegetables.
Shellfish: Shellfish, including oysters, clams, and mussels, are potent sources of minerals and are filled with selenium, zinc, copper, and iron.
Swallowing 6 medium-sized oysters (approx 84 grams) protects your daily requirements for zinc and copper and delivers about 30% and 22% of your daily requirements for selenium and iron, respectively.
Zinc is a nutrient that’s important for the resistant process, DNA production, cellular unit, and the display of proteins.
Pregnant and breastfeeding ladies, those with gastrointestinal illness, people taking certain medicines, adolescents, and older grown-ups are populations that are at stake for zinc deficiency, which can damage resistant response, hinder growth and expansion, and improve infection risk.
Shellfish supply a centralised source of zinc and create a smart option for those at risk of creating a weakness in this important nutrient.
Cruciferous vegetables:
Eating cruciferous vegetables such as cauliflower, broccoli, Swiss chard, and Brussels nodes, is associated with multiple fitness benefits, including the removal of chronic illness.
These fitness advantages are instantly related to the nutrient thickness of these veggies, including their unique attention to minerals.
In addition to sulfur, cruciferous vegetables are a sound source of many other minerals, such as magnesium, potassium, manganese, and calcium.
Organ meats
Although not as famous as protein bases like chicken and steak, organ meats are amongst the most mineral-dense meals you can consume.
For instance, a slice (approx 85 grams) of beef liver protects your daily copper requirements and supplies about 55%, 41%, 31%, and 33% of your day-to-day requirements for selenium, zinc, iron, and phosphorus, respectively. Additionally, organ meats are increased in protein and vitamins, such as vitamin B12, vitamin A, and folate
Eggs
Eggs are usually directed to as nature’s multivitamin — and for good reason. Whole eggs are prosperous in nutrients and supply many important minerals.
They’re high in iron, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium, as nicely as many vitamins, beneficial fats, antioxidants, and proteins.
Although many individuals bypass egg yolks due to their cholesterol content, the yolks have almost all of the vitamins, minerals, and other useful combinations, so make sure to eat the whole egg, not just the white.
Beans
Beans are understood for being loaded with fibre and protein, but they also occur to be a great source of minerals, including potassium, manganese, calcium, magnesium, iron, phosphorus, copper, and zinc
However, beans also have antinutrients, including phytates, which can reduce nutrient absorption. Still, a study has demonstrated that properly preparing beans by growing or soaking and boiling them can assist improve the bioavailability of minerals.
Cocoa
Adding cocoa to smoothies, chewing on a piece of dark chocolate, or spreading your yoghurt with cacao nibs are fulfilling methods to boost your mineral intake.
Although they’re not usually associated with being nutrient-dense, cocoa creations are loaded with minerals. Cocoa and cocoa creations are particularly rich in magnesium and copper.
Magnesium is required for energy presentation, blood pressure regulation, nerve function, blood sugar management, and more.
Copper is required for proper development and growth, carbohydrate metabolism, iron absorption, and red blood cell ( aka RBC) formation, in addition to many other crucial bodily functions.
Avocados
Avocados are creamy fruits filled with healthy fats, fibre, vitamins, and minerals. They’re extremely rich in magnesium, potassium, manganese, and copper.
Potassium is a mineral that’s important for blood pressure control and heart health. Investigations have indicated that diets high in potassium-rich meals like avocados may assist decrease your risk of heart illness and stroke.
A review of 33 investigations that had 128,644 individuals found that higher potassium intake was linked with an approx 24% reduced chance of stroke and reduction in heart illness risk elements like high blood pressure levels
Berries
Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, and raspberries, are not only delicious but also an incredible source of crucial minerals.
Berries are a useful source of potassium, magnesium, and manganese. Manganese is a mineral that’s essential for several metabolic processes involved in energy metabolism, as well as resistant and nervous system process
This mineral is also required for the growth and care of healthy bone and connective tissues, as well as the result of antioxidants that assist protect cells against oxidative injury.
Yogurt and cheese
Dairy products, including yogurt and cheese, are some of the numerous common origins of calcium in the diet. Calcium is required to support a healthy skeletal system and is important for your nervous method and heart fitness.
Investigations show that many individuals, particularly older grown-ups, do not consume enough calcium in their food.
Adding high-quality dairy like yogurt and cheese to your food is a good way to boost your intake of calcium, as well as other minerals such as potassium, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium
Nevertheless, many individuals are impatient with dairy products. If you cannot eat dairy, many other meals contain calcium, including beans, nuts, and leafy greens.